Basal Cell Carcinoma
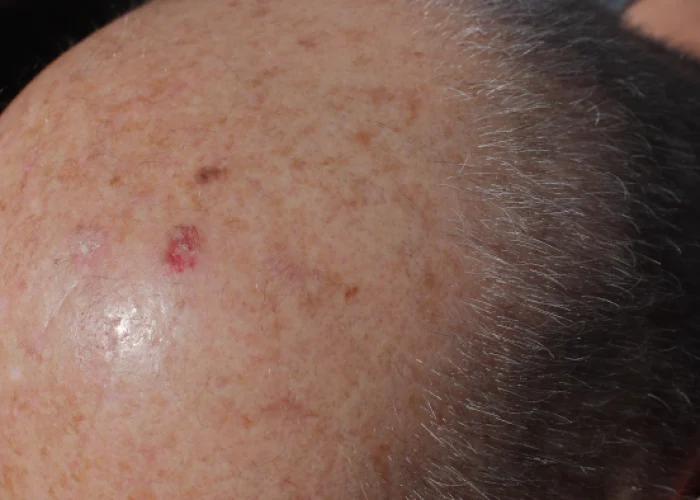
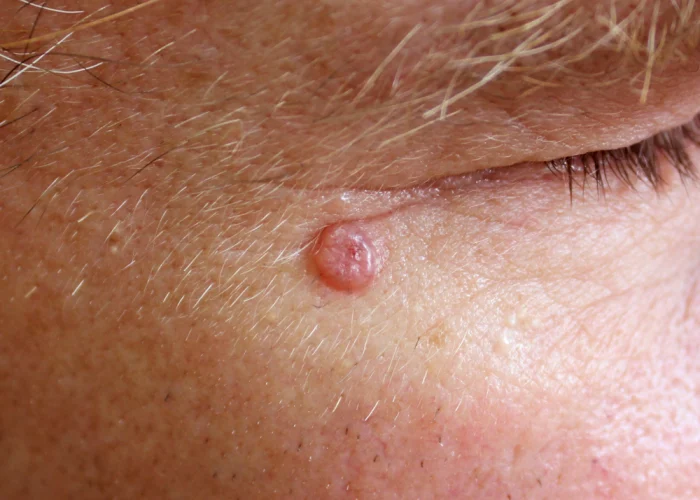
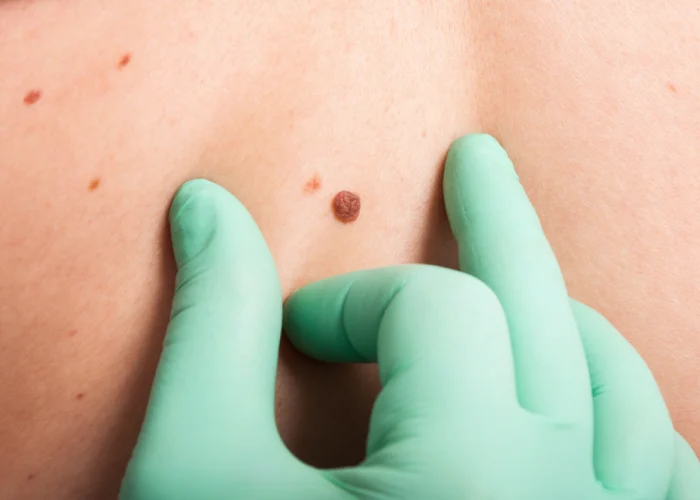
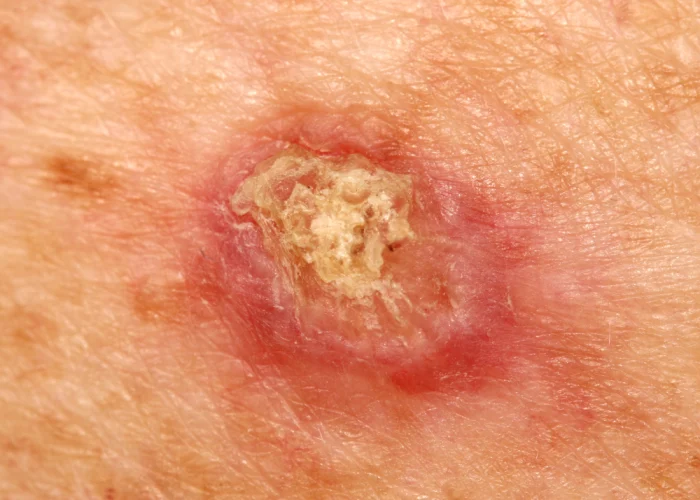
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a type of skin cancer that typically develops in the basal cells, which are located in the lowest layer of the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. BCC most commonly occurs in areas of the body that are exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, scalp, ears, shoulders, and back. However, it can also develop in non-sun-exposed areas. BCC often presents as a slow-growing, flesh-colored or pinkish bump that may have a pearly or translucent appearance. It can also appear as a sore that does not heal or as a scaly or crusty patch. A dermatologist diagnoses basal cell carcinoma by performing a skin biopsy. The biopsy helps determine the extent of the cancer and classify it as superficial or invasive.